
Temporary accounts (or nominal accounts) include all of the revenue accounts, expense accounts, the owner’s drawing account, and the income summary account. Generally speaking, the balances in temporary accounts increase throughout the accounting year. At the end of the accounting year the balances will be transferred to the owner’s capital account or to a corporation’s retained earnings account. As seen in the journal entry above, the Cost of Sales Expense account is debited by $8,600, and $1,600 is credited to the Purchases account. Then the inventory account is credited with $7,000 ($8,600 Cost of Sales – $1,600 purchase). Notice that, the respective $1,600 & $7,000 credits to purchases and inventory equal the $8,600 debit to cost of sale.
- The inventory of a manufacturer should report the cost of its raw materials, work-in-process, and finished goods.
- For example, interest earned by a manufacturer on its investments is a nonoperating revenue.
- The permanent accounts are sometimes described as real accounts.
- For example, a company will have a Cash account in which every transaction involving cash is recorded.
- Generally, expenses are debited to a specific expense account and the normal balance of an expense account is a debit balance.
- There are unadjusted, adjusted, and post-closing trial balances.
Examples of Debits and Credits in a Corporation
There are unadjusted, adjusted, and post-closing trial balances. Learning about financial entries is key for keeping accurate records. Real-life examples show us how transactions can affect accounts. They highlight the importance of understanding journal entries in everyday business. The balance sheet accounts are referred to as permanent because their end-of-year balances will be carried forward to the next accounting year. The permanent accounts are sometimes described sales normal balance as real accounts.
Sales Returns and Allowances: Definition
This is occurring even though the transaction is recorded with an entry to Cash (a permanent asset account) and an entry to Consulting Revenues (a temporary account). Again, you need to understand that the $500 credit entry to Consulting Revenues is causing a $500 increase in a permanent account that is part of owner’s equity or stockholders’ equity. Generally, expenses are debited to a specific expense account and the normal balance of an expense account is a debit balance.
After the Temporary Accounts are Closed

This account has a negative or debit balance, so it is also called a contra-revenue account. Revenue accounts show money made from business activities and have a credit balance. This means increases in revenue boost equity through credits. Meanwhile, expense accounts reflect costs in making revenue, typically having a debit balance. Recording an expense as a debit shows its reducing effect on equity.

When Cash Is Debited and Credited
Accounts, such as earned interest, sales discounts, Food Truck Accounting and sales returns, are considered temporary accounts for accounting purposes. However, in general, companies consider other relevant factors while determining the accounting treatment of a business transaction. By starting each year with zero balances, the income statement accounts will be accumulating and reporting only the company’s revenues, expenses, gains, and losses occurring during the new year. It’s essentially what’s left over when you subtract liabilities from assets.
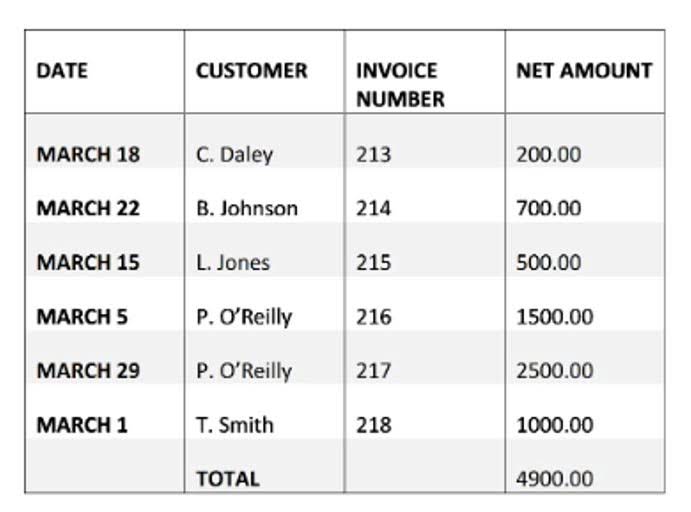
If this is done for every transaction and without errors, then all the amounts appearing in the accounts will have the total amount of debits equal to the total amount of credits. For reference, the chart below sets out the type, side of the accounting equation (AE), and the normal balance of some typical accounts found within a small business bookkeeping system. A liability account on the books of a company receiving cash in advance of delivering goods or services to the customer. The entry on the books of the company at the time the money is received in advance is a debit to Cash and a credit to Customer Deposits. Accounts that are closed at the CARES Act end of each accounting year. Included are the income statement accounts (revenues, expenses, gains, losses), summary accounts (such as income summary), and a sole proprietor’s drawing account.
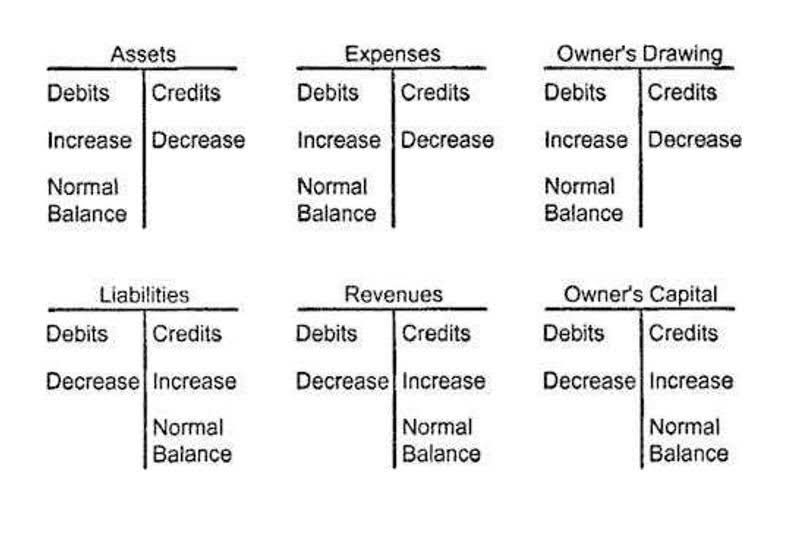
This means that the cost of sending the cars to dealers and the cost of the labor used to sell the car would not be included in the cost of sales calculation. The term cost of sales is more likely to be used by manufacturers. An example of a sales discount is when a buyer is entitled to a 1% discount in exchange for paying within 10 days of the invoice date, rather than the normal 30 days. This is often stated in the invoice as “1% 10/Net 30” terms. Based on the rules of debit and credit (debit means left, credit means right), we can determine that Assets (on the left of the equation, the debit side) have a Normal Debit Balance. Overshooting in sales is caused due to overstating of sales returns and allowances.
